Maintenance & Parts Support
Keep Your Industrial Oven Running
Service engineers, spare parts, and on-site supportfor ZonHoo industrial ovens.
Table of contents
Introduction
Industrial oven maintenance is not only “fixing faults.” It is risk control—temperature stability, airflow consistency, safe operation, and wear parts that drift until quality drops or downtime happens. As the manufacturer, ZonHoo supports your team with practical PM routines, correct part matching, and efficient troubleshooting—so your line stays productive and predictable.
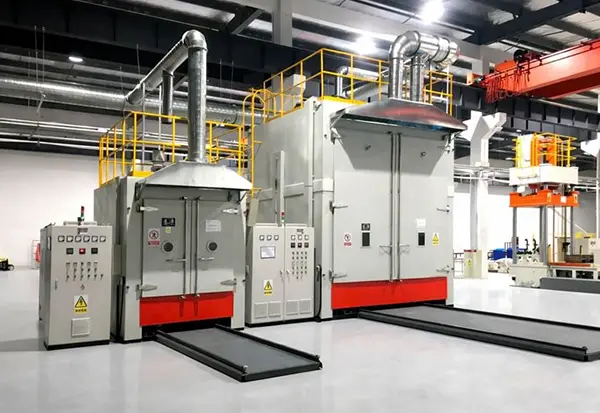
1. Oven types and what maintenance focuses on
Different oven configurations fail in different ways. Use the guidance below to prioritize inspections, wear items, and spares planning—especially when uptime and delivery schedules are critical.
Batch / Box Ovens
Typical use: curing, drying, heat aging, stress relieving (batch production).
Maintenance focus: heater health, airflow cleanliness, door seal integrity, sensor stability, terminal tightening (power OFF).
High-risk spares: heater elements, contactors/SSR/SCR (model-specific), process sensor (TC/RTD), door gasket kit, fan bearings.
Walk-In / Truck-In Ovens
Typical use: large parts, carts/racks, low handling time, high throughput by load size.
Maintenance focus: door alignment and sealing, airflow balance across the chamber, fan performance, hot-spot insulation checks, safety interlocks.
High-risk spares: door hardware + gaskets, fan motor/bearing kit, limit switches, key power components, chamber sealing materials.
Conveyor Ovens (Continuous)
Typical use: continuous drying/curing/heating with stable takt time.
Maintenance focus: conveyor tracking/tension, wear rails, drive system, chain/belt wear, airflow path and filters, cabinet heat management.
High-risk spares: chain/belt segments, wear rails, sprockets/rollers, drive components, fan bearings, sensors at infeed/outfeed.
High-Temperature / Special Atmosphere Ovens (as applicable)
Typical use: higher process temperatures or controlled atmosphere requirements.
Maintenance focus: insulation aging, heater load management, sensor drift, sealing, safety device verification, cabinet thermal stress.
High-risk spares: high-temp heaters/wiring sets, over-temp device, sealing kits, critical electrical switching components.
We have helped companies worldwide improve industrial oven maintenance.

Competitive price
3000+
Customers
120+
Countries
150+
Partners
200+
OEM Parts SKUs
2.Basic Recommended Preventive Maintenance Plans
A structured PM plan reduces unplanned downtime and protects product quality. Use this as a baseline, then adjust by operating hours, max temperature, load type, and environment (dust, solvent, humidity).
Inspection schedules
Daily/Shift: visual check, abnormal noise/odor, door seal contact, alarm review
Weekly: airflow intake cleanliness, fan noise/vibration, filter condition, conveyor tracking (if any)
Monthly: inspect cables/terminals (power OFF), hinges/latches, hot-spot check around panels
Quarterly/Semi-annual: verify safety devices, inspect airflow path, lubrication plan execution
Annual: planned shutdown inspection + wear parts replacement + restart verification
Core maintenance tasks
Clean airflow path: guards, plenums, ducts, intake zones; remove dust and buildup
Check heating system: heaters, wiring, grounding, switching components condition
Verify fans/motors: bearings, alignment, impeller cleanliness, mounting tightness
Protect sealing: door gaskets, latches, hinges to prevent heat loss and instability
Conveyor ovens: tension/tracking, wear rails, drive inspection, lubrication points
Documentation and records
Log operating hours, max temperature exposure, cycle counts, and alarm history
Maintain spare parts register: part no., revision, lead-time, stocking level
Record replacements with date, cause, photos (helps root-cause analysis)
Keep as-built manuals, wiring diagrams, and parts lists accessible to MRO teams
Standardize PM checklists to reduce shift-to-shift variation
Safety and competency
Lockout/Tagout (LOTO) before electrical or mechanical work
Hot surface control: cool-down verification and PPE
Verify safety functions after maintenance: interlocks, E-stop, over-temp protection
Electrical work by qualified personnel; torque checks done power OFF
Follow site EHS requirements for solvent/flammable processes (if applicable)
Consistent PM is the fastest way to improve uptime, reduce MRO surprises, and keep temperature performance stable across production shifts.
3. Key oven components
Heating system
Heater elements/heater banks, power switching (contactor/SSR/SCR), wiring, grounding, and over-temperature protection. Stable heating response prevents cycle drift and quality variation.
Air circulation & airflow path
Fans, motors, bearings, impellers, ducts, baffles, filters, and guards. Airflow loss is a common hidden cause of uneven temperature and slow ramp-up.
Insulation & chamber integrity
Panel insulation, hot spots, structural interfaces, and leak points. Chamber integrity improves energy efficiency and repeatability.
Doors, seals & hardware
Gaskets, hinges, latches, and door switches. Small mechanical wear can create large heat loss and unstable temperature zones.
Sensors & safety devices
Process sensors (TC/RTD), over-temp devices, limit switches, interlocks, and E-stop. Always verify safety functions after maintenance.
Conveyor system (if applicable)
Drive, tracking, chain/belt, wear rails, rollers, and lubrication points. Wear typically appears as tracking drift, noise, and throughput instability.
4. Common problems and troubleshooting
Use the symptoms below for quick triage. For faster resolution, escalate to ZonHoo with serial number, photos/videos, alarm screenshots, and basic measurements.
Slow heat-up or cannot reach setpoint
Likely causes: heater degradation, power switching fault, airflow blockage, door seal leakage.
Quick checks: compare zone behavior, inspect airflow path/filters, verify door gasket contact, check visible signs of overheating in the control cabinet (power OFF inspection only).
Temperature fluctuation or product variation
Likely causes: sensor drift, airflow imbalance, fan performance drop, hot spots from insulation/seal wear.
Quick checks: inspect fans/impellers, confirm sensor condition and mounting, check for chamber leaks, verify consistent loading practices.
Frequent alarms or unexpected stops
Likely causes: safety device triggered, loose terminals, cabinet overheating, door switch misalignment, unstable power components.
Quick checks: review alarm timestamps, confirm cabinet ventilation, inspect terminals (power OFF), check door switch alignment and interlock function.
Preventive Measures
- Keep airflow clean—filters, intake zones, and ducts
- Replace door seals before leaks become performance problems
- Track cycle hours and max temperature exposure, not only calendar time
- Stock critical spares to eliminate “waiting for parts” downtime
- Standardize PM checklists and maintenance logs across shifts
Planned maintenance plus OEM spares planning is the most cost-effective path to predictable uptime and stable process results.
Let’s talk about how we can support your thermal processing goals. Contact our team to explore the right solution for your needs.