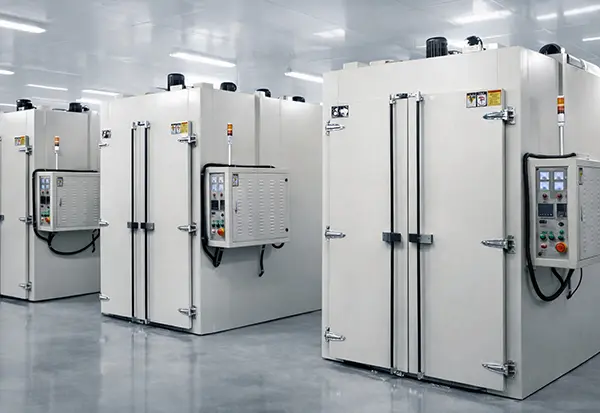
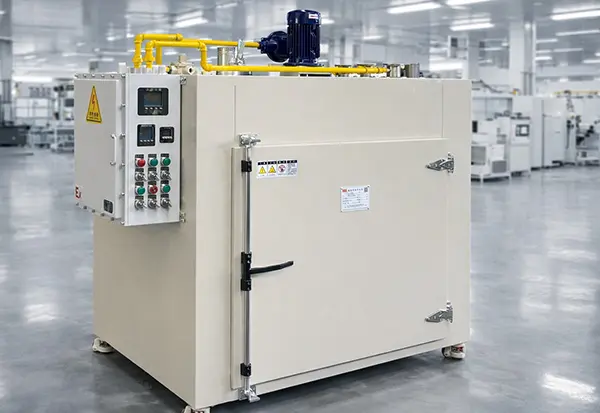
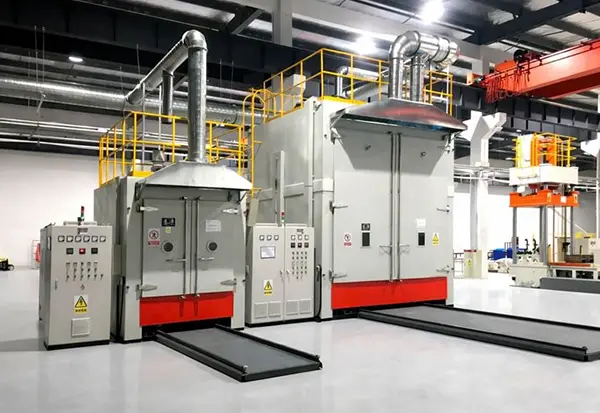
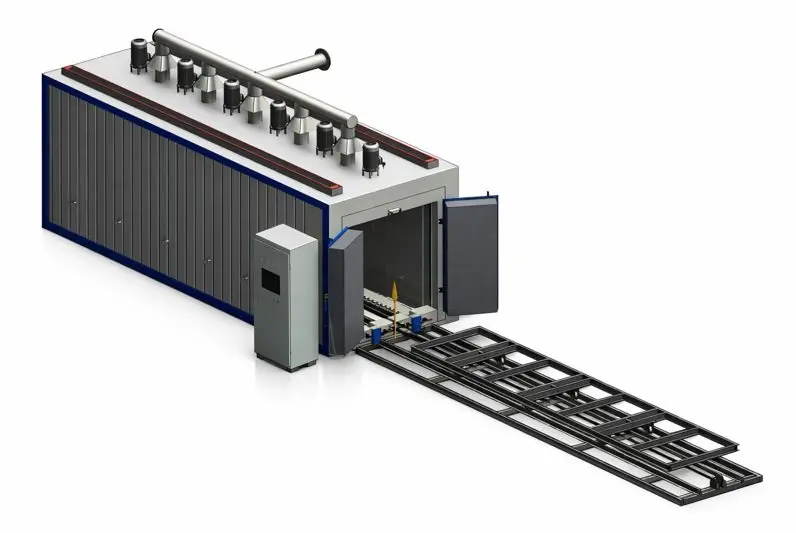
Forced Convection Curing Oven
ZonHoo forced convection curing oven systems use engineered air recirculation to deliver repeatable curing results when temperature uniformity and process stability drive yield. We configure airflow distribution (ducting, baffles, and return paths), sensing strategy, and controls to match your RFQ—from compact batch chambers to production-scale systems.
As a manufacturer supporting OEM/ODM, we start with an engineering review so your team gets a procurement-ready specification, defined acceptance scope, and predictable lead time.
What a Forced Convection Curing Oven Is
A forced convection curing oven is a curing system that uses controlled air movement to transfer heat consistently to parts, fixtures, and assemblies. Compared with “natural convection” heating, forced-air circulation reduces hot/cold zones, improves heat penetration across mixed geometries, and helps stabilize curing results across batches or shifts.
This approach is commonly chosen when your process requires defined uniformity expectations, repeatable ramp/hold behavior, and verification-ready documentation.
Uniformity Drivers (Why Curing Results Drift)
Curing variation is usually not caused by setpoint alone—it is caused by how heat reaches the load. Common drift factors include load density, part mass differences, shadowing from fixtures, blocked airflow paths, and uneven return flow that creates cold pockets.
An effective air circulation curing oven design starts by understanding your load pattern, spacing, and the real thermal “worst case,” then configuring recirculation paths and sensing to stabilize results.
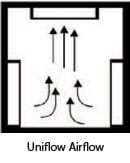

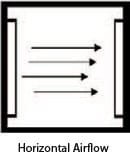

Airflow Engineering
Forced convection performance depends on airflow architecture—not just fan size. ZonHoo configures distribution and return flow based on your part geometry, spacing, and throughput goals:
- Ducting & baffles: guide supply air to target zones and reduce stagnant regions.
- Supply/return path balance: prevents short-circuit flow and supports consistent heating across the working area.
- Recirculation strategy: tuned for load density so heat transfer remains stable from batch to batch.
- Air velocity approach: supports surface heat transfer without compromising handling or fixture constraints (process-defined).
Controls & Sensing Strategy
To standardize curing outcomes, controls must match the physics of your load:
- Recipe-based control: ramp/hold steps and dwell logic aligned to your curing window.
- Sensing placement: thermocouple strategy matched to load zones and worst-case areas.
- Alarms & interlocks: protects process stability and supports safer operation (as configured).
- Optional records: cycle logs and event history for traceability and internal QA.
Verification & Acceptance
If uniformity drives yield, verification must be part of the scope—not an afterthought. We support project-defined acceptance checks such as temperature verification planning, documentation scope alignment, and record outputs required by your internal standards.
For engineering teams, the goal is a temperature mapping ready curing oven configuration; for procurement, it’s a clear acceptance scope that can be quoted and approved.
System Configurations
A high uniformity curing oven can be configured for different production modes without changing the forced convection logic:
- Batch configuration: flexible scheduling and mixed-load curing with defined recipes.
- Walk-in configuration: larger racks and higher batch volume with service-friendly access.
- Continuous configuration (integration-ready): suited to stable throughput where upstream/downstream handling is standardized (project-defined).
Typical Applications
- Adhesive curing where repeatability affects bond strength
- Composite post-cure cycles requiring stable heat distribution
- Electronics potting/encapsulation curing with controlled dwell behavior
- Coating/finish curing where uniformity impacts appearance and hardness
- Powder coating curing when mixed geometries require airflow consistency
- Industrial assemblies where documented cycles support QA requirements
RFQ Checklist
To quote a custom forced convection curing oven accurately, include:
- Cure temperature range, ramp/hold steps, and dwell time requirements
- Largest part size, typical mass range, and fixture/rack/hanger layout
- Load density and spacing constraints (where airflow may be blocked)
- Throughput goals (batches/hour or takt time; continuous line speed if applicable)
- Desired temperature uniformity expectation and acceptance scope
- Controls/records requirements (recipes, alarms, data logging)
- Site utilities, footprint constraints, and integration interfaces
- Forced-air recirculation (process-defined)
- Uniform airflow distribution strategy
- Temperature uniformity focus (mapping-ready)
- Multi-zone sensing & control options
- Recipe control + alarms (optional records)
- Load density / spacing engineering review
- Acceptance checks & documentation scope
- Integration-ready I/O & safety interlocks (as configured)
Let’s talk about how we can support your thermal processing goals. Contact our team to explore the right solution for your needs.